Quercetin -Shield Your Body with the Antioxidant Power of Quercetin.
May 18, 2025
Elevate Your Mental Clarity and Focus – Experience the Power of Cerebrolysin.
May 18, 2025What is Chelation?
Chelation is a process in which a substance, called a chelator, binds to metal ions in the body, forming a stable, soluble complex that can be excreted through urine or feces. This process is primarily used to remove toxic metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic from the body, but it can also help in balancing essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron in certain medical situations.
How Does Chelation Work?
Chelation therapy involves the use of chelating agents, which are molecules designed to bind tightly to metals in the body. These agents grab hold of metal ions and prevent them from interacting with biological systems, thereby neutralizing their toxic effects. The chelated metal is then safely excreted through urine or stool.
Health Benefits of Chelation
-
Heavy Metal Detoxification: Chelation therapy is most commonly used to treat heavy metal poisoning. It is effective in removing toxic metals such as:
- Lead: Exposure to lead can cause neurological damage, particularly in children.
- Mercury: Mercury poisoning can result from contaminated seafood, industrial exposure, or dental fillings.
- Arsenic: A naturally occurring element found in contaminated water and some pesticides.
By binding to these metals, chelation helps prevent them from accumulating in tissues and organs, reducing the risk of long-term damage.
-
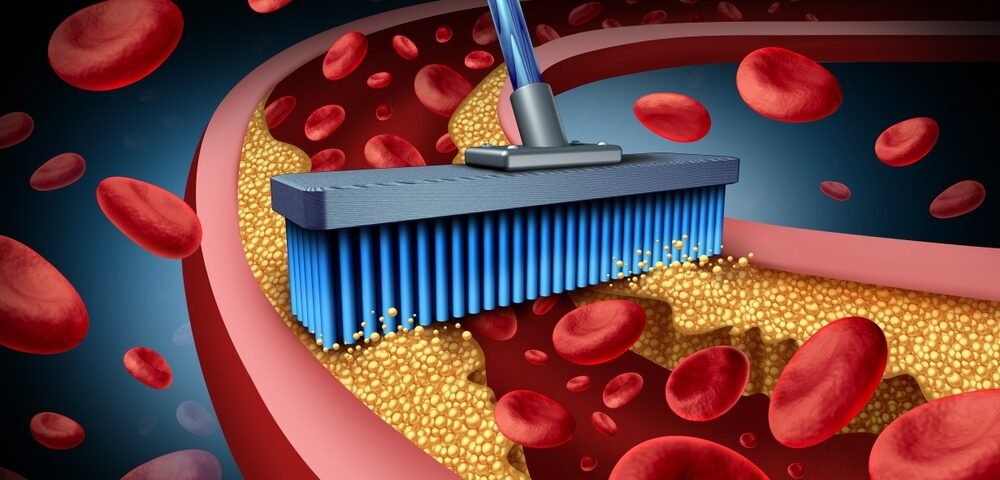
Improving Cardiovascular Health: Chelation therapy is sometimes used as a treatment for atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) or to improve circulation. EDTA chelation is thought to help by reducing calcium buildup in blood vessels, which may reduce plaque formation and improve blood flow.
-
Brain Health and Cognitive Function: There is emerging evidence suggesting that chelation might help in cases of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, by removing metals like copper and iron, which may contribute to oxidative damage in the brain.
-
Detoxification and Liver Support: Chelation can also help support the liver by removing toxic metals that may have accumulated over time. This can lead to enhanced overall detoxification in the body and improved organ function.
-
Balancing Essential Minerals: Chelation therapy may be used to correct mineral imbalances, particularly when minerals like calcium, magnesium, or iron are either too high or low in the body. Proper mineral balance is crucial for optimal cellular function.
Safety and Considerations
While chelation therapy can be highly effective in removing toxic metals from the body, it should be done under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Improper use of chelation agents can lead to:
- Mineral Deficiencies: Since chelation can also bind to essential minerals, it may lead to deficiencies in vital nutrients like calcium, magnesium, or zinc.
- Kidney Damage: Excessive or improper use of chelation agents can overwhelm the kidneys, leading to potential kidney damage.
- Side Effects: Common side effects can include nausea, fatigue, headache, or dizziness. More serious side effects can occur if the therapy is not managed correctly.
Conclusion
Chelation therapy is a powerful tool for detoxifying the body by removing harmful heavy metals and supporting overall health. While it is primarily used to treat heavy metal poisoning, it also shows promise for supporting cardiovascular health, brain function, and detoxification. However, it is important to consult a healthcare provider before considering chelation therapy, particularly for non-medical uses, to ensure safety and proper management.