High Dose Vitamin C: Your Ultimate Immune System Boost!
May 18, 2025
Power up your body with Selenium: The antioxidant hero that supports immunity, skin, and overall wellness!
May 18, 2025What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for maintaining overall health. Unlike most vitamins, it can be synthesized by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D plays a vital role in calcium absorption, bone health, immune function, and more. It is also found in foods such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and eggs.
Health Benefits of Vitamin D
- Bone Health and Calcium Absorption: Vital for absorbing calcium and phosphorus, vitamin D helps prevent bone disorders like osteoporosis, rickets, and osteomalacia.
- Immune System Support: Enhances immune cell function and helps reduce the risk of infections and autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Mood and Mental Health: Supports serotonin production, potentially reducing the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Cardiovascular Health: May lower the risk of hypertension and heart disease by regulating blood pressure and improving blood vessel function.
- Cancer Prevention: Some research links adequate vitamin D levels to reduced risk of cancers like colorectal, breast, and prostate.
- Muscle Function and Strength: Helps maintain healthy muscle fibers, improve strength, and reduce the risk of falls in older adults.
How is Vitamin D Produced and Obtained?
- Sunlight Exposure: The skin produces vitamin D when exposed to UVB rays. Just 10–30 minutes of sun exposure a few times per week is often enough, though factors like skin tone and location can affect this.
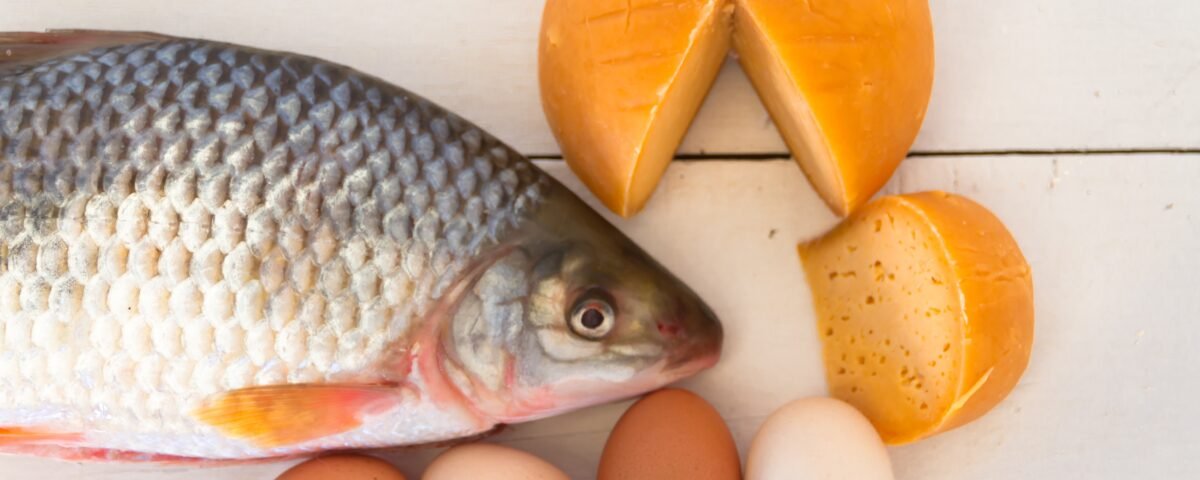
- Dietary Sources:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Egg yolks
- Fortified foods (milk, orange juice, cereals)
- Cheese and butter (in smaller amounts)
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Bone Pain and Muscle Weakness: Can lead to fractures and musculoskeletal discomfort.
- Fatigue and Mood Disorders: Linked to depression, fatigue, and seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Increased Risk of Infections: A weak immune system makes the body more susceptible to colds and flu.
- Osteoporosis and Rickets: Long-term deficiency may cause soft or weak bones in both children and adults.
Who is at Risk of Vitamin D Deficiency?
- Older adults with reduced skin synthesis ability
- People with darker skin, due to higher melanin levels
- Individuals with limited sun exposure or living in northern regions
- Those with conditions like Crohn’s, celiac disease, or obesity
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women with increased nutrient needs
Safety and Side Effects
While vitamin D is essential, too much can be harmful. Excessive intake may lead to:
- Hypercalcemia: High calcium levels causing nausea, vomiting, weakness, and kidney issues.
- Kidney Stones: Due to excess calcium in the urine.
- Tissue Calcification: Calcium deposits in organs like the heart and kidneys.
Conclusion
Vitamin D is crucial for bone strength, immune defense, heart health, and mental wellness. Sun exposure, diet, or supplements can help maintain healthy levels. If you're unsure about your vitamin D status, a simple blood test and medical consultation can help determine if supplementation is right for you.